langerhanscellhistiocytosis.org – The Islamic calendar, also known as the Hijri calendar, is a lunar calendar used by Muslims around the world to determine the proper days on which to observe religious events and festivals. This calendar is based on the moon’s phases and consists of 12 months, with each month beginning when the first crescent moon is sighted. The Islamic calendar is significant in guiding the Muslim community in their religious practices, providing a framework for the observance of holy days and rituals.
Understanding the Lunar-Based Islamic Calendar
The Islamic calendar is purely lunar and does not rely on the solar year. This means that it does not correspond to the seasons in the way that solar calendars do. Since the lunar year is approximately 11 days shorter than the solar year, the Islamic calendar shifts with respect to the Gregorian calendar, which is solar-based. This shift allows Muslims to experience the holy months in different seasons over the course of their lives.
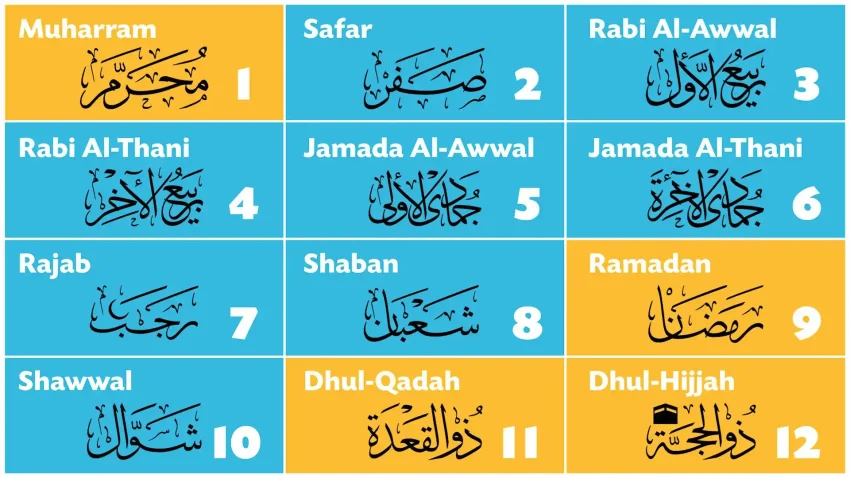
The months of the Islamic calendar are as follows:
- Muharram
- Safar
- Rabi’ al-Awwal
- Rabi’ al-Thani
- Jumada al-Ula
- Jumada al-Thani
- Rajab
- Sha’ban
- Ramadan
- Shawwal
- Dhu al-Qi’dah
- Dhu al-Hijjah
The Significance of the Islamic Calendar in Religious Observances
Ramadan
One of the most significant events in the Islamic calendar is the month of Ramadan, the ninth month, during which Muslims fast from dawn until sunset. Ramadan is a time for spiritual reflection, self-improvement, and increased devotion and worship. The end of Ramadan is marked by the celebration of Eid al-Fitr, a joyous occasion when Muslims gather for communal prayers, exchange gifts, and share meals.
Hajj
The Hajj, or pilgrimage to Mecca, is another key event in the Islamic calendar, taking place in the 12th month, Dhu al-Hijjah. It is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and is obligatory for all adult Muslims who are physically and financially able to perform it at least once in their lifetime. The Hajj culminates in the festival of Eid al-Adha, during which Muslims worldwide commemorate the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God.
Other Observances
The Islamic calendar also marks other significant events, such as the birth of Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him), known as Mawlid or Eid Milad un Nabi, which falls in the third month, Rabi’ al-Awwal. Additionally, the 10th of Muharram, Ashura, is observed by many Muslims, commemorating the day that God saved Prophet Musa (Moses) and the Israelites from Pharaoh.
The Role of the Islamic Calendar in Muslim Life
The Islamic calendar plays a crucial role in the daily lives of Muslims, guiding them in their religious observances and providing a sense of community and shared identity. It helps to maintain a connection with the historical events and teachings of Islam, ensuring that the traditions and practices are preserved and passed down through generations.
In conclusion, the Islamic calendar is not just a means of marking time; it is a guide for Muslims to live in accordance with their faith. It serves as a reminder of the importance of spiritual growth, community, and the remembrance of God. Through the observance of the Islamic calendar, Muslims around the world are united in their religious practices, regardless of the time zone or geographic location.